What Is the F Code in CNC? Feed Rate Explained
What Is the F Code in CNC? Feed Rate Explained
If you're learning CNC programming or diving deeper into G-code, you've probably seen the F code used frequently. But what exactly does the F code in CNC mean?
In CNC machining, the F code defines the feed rate—one of the most critical parameters in ensuring accurate, efficient, and safe machining.
This article explains what the F code does, how it's used, and why it matters in your CNC programs.
⚙️ What Is the F Code in CNC?
The F in CNC programming stands for Feed Rate. It tells the machine how fast the cutting tool should move along its programmed path during a machining operation.
CNC F Code Definition:
F = Feed rate, expressed in units per minute (e.g., inches per minute or millimeters per minute)
The F code is always paired with a number, like F100, which means:
- F100 = Move at 100 inches per minute (on imperial systems)
- F250 = Move at 250 millimeters per minute (on metric systems)
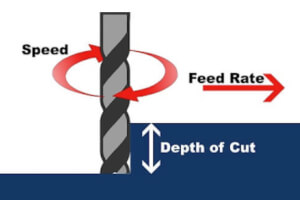
📏 Feed Rate vs. Spindle Speed
It's easy to confuse feed rate (F) with spindle speed (S), but they are very different.
- F (Feed Rate): Speed the tool travels along the workpiece
- S (Spindle Speed): Speed at which the spindle rotates (RPM)
Both are essential, but the F code controls the linear movement speed, while S controls rotational speed.
🛠️ Common Examples of F Code in CNC Programs
Here are some basic examples of the F code in real G-code snippets:
G1 X2.0 Y1.0 F150
- G1: Linear interpolation
- X2.0 Y1.0: Move to coordinates
- F150: Use a feed rate of 150 units per minute
G1 Z-1.0 F30
Move the tool downward into the material at 30 inches/min
📐 When and Where to Use F Code
The F code is typically used during:
- Milling
- Drilling
- Turning
- Tapping
- Engraving
It's most relevant when using G1 (linear move), G2/G3 (circular moves), or any cutting motion where tool movement affects material removal.
📉 What Happens If Feed Rate Is Too Fast or Too Slow?
Feed rate directly affects part quality, tool wear, and machining safety.
Too Fast:
- Tool may break
- Poor surface finish
- Machine chatter or vibration
Too Slow:
- Wasted cycle time
- Excessive tool wear from heat buildup
- Burn marks on the part (especially in wood or plastic)
💡 Pro Tip: Use Recommended Feed & Speed Charts
Always refer to the tool manufacturer’s recommendations for:
- Material type (e.g., aluminum vs. steel)
- Cutter diameter
- Depth of cut
- Type of tool (end mill, drill, insert, etc.)
Modern CAM software can also auto-generate optimal F and S codes based on tool libraries.
🧠 Summary: Why the F Code Matters in CNC
The F code in CNC machining is crucial for controlling how quickly the tool moves through material. It affects:
- Cutting efficiency
- Tool longevity
- Surface finish
- Overall part accuracy
Understanding and using the right F code ensures that your machine operates safely, efficiently, and consistently—whether you're making simple cuts or complex 5-axis parts.
🔎 FAQs About CNC F Code
Q: Do I need to re-enter F code for every move?
A: No. Once set, the feed rate stays active until changed by another F command.
Q: Can I use decimals in F code?
A: Yes, you can write feed rates like F12.5 for finer control.
Q: Is F code always in inches/minute?
A: Not necessarily—it depends on whether the program uses G20 (inches) or G21 (millimeters).


